Vascular Disease
Our clinic specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of Venous Disease and Peripheral Arterial Disease. There are several treatment options for these conditions. We will do an assessment and determine which one is best for your situation. Please read below for answers to the most commonly asked questions.
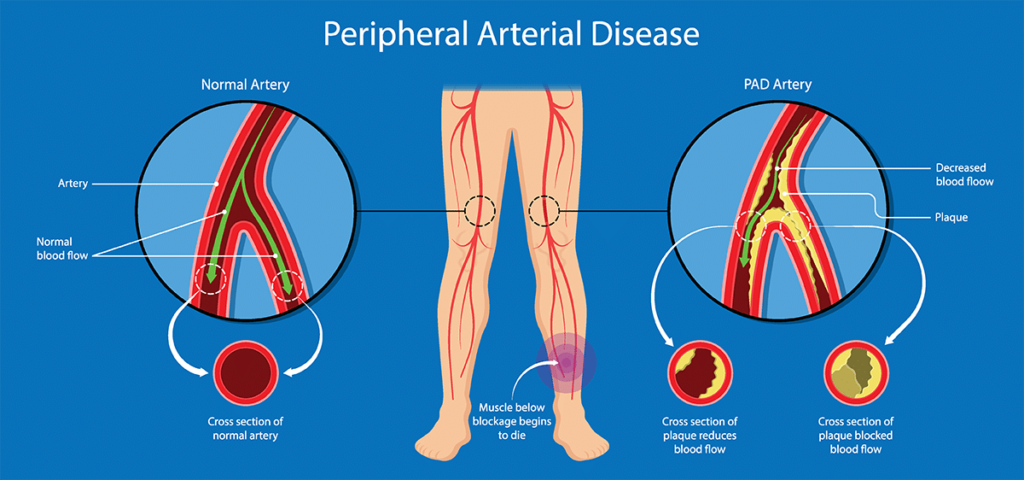
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Our clinic specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of PAD.
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is one of the most common vascular conditions affecting lower extremities. Usually, the underlying cause of PAD is atherosclerosis, which is also the most common cause of heart attacks and strokes. Atherosclerosis is the condition in which the arteries can get clogged by fatty plaques limiting the blood supply to the extremities or organs.
- Over 20% of population will suffer from PAD after the age of 75.
- There are near 150,000 amputations each year due to PAD.
- Smoking will increase your risk by 4 fold.
- Many patients with PAD can be asymptomatic.
- Pain and cramping of calf and thigh muscles after exercising or walking (intermittent claudication)
- Hair loss and changing of the color of the affected leg (shiny skin)
- Coldness in your legs or feet
- Painful sores on your toes and feet that won’t heal
- Hair loss or slower hair growth on your feet and legs
- Slower growth of your toenails
- Erectile dysfunction in men
- In later stages of the disease, pain can be present also at rest
- Smoking
- High cholesterol (hyperlipidemia)
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Age
- Family history of peripheral arterial disease, heart disease or stroke
- High levels of amino acid homocysteine (found in meat).
- Severe leg ischemia. It starts from developing toe ulcers, which are very painful and difficult to heal. If untreated, this can lead to death of the affected tissue (gangrene). At this point the treatment would be an amputation of the affected segment resulting in various complications.
- Stroke and heart attack. Peripheral arterial disease is a systemic disorder affecting not only the lower extremity vessels but also other vessels in the body including the coronary arteries and vessels of the brain. People diagnosed with peripheral arterial disease have a higher likelihood of having coronary arterial disease that can lead to heart attack. If the
vessels of the brain are affected, this can lead to a stroke.
- Ankle-Brachial Index or ABI Test
This is a quick and simple test, which uses blood pressure cuffs to measure blood pressure in your arms and different segments of the legs. Usually, blood pressure in the arms and legs should not be different. If the blood pressure in the legs is significantly decreased compared to
the arms, it could be due to atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels of the leg. This test can be
repeated multiple times and is a valuable tool for PAD screening. - Duplex Ultrasound is another important diagnostic test for PAD screening. It is used to visualize
the inner side of the vessels, measure the velocity of the blood flow, and determine whether there are plaques in the arteries. The ultrasound study is performed by specially trained and
certified sonographers (registered vascular technologists – RVT). This test is also non-invasive, safe, and can be repeated multiple times. - An angiogram is an invasive surgical procedure using an X-ray to image blood vessels. For this
procedure, a special solution (dye) is injected into the arteries. X-ray images are taken during
the injection of the dye helping the surgeon to see every single vessel (that the dye penetrated
into) in detail. If a vessel does not get enough dye, a plaque would be suspected, and the surgeon can decide on the best treatment option. Angiogram is a very accurate test and is considered a gold standard for the diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease. - Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) and Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Tests
CTA and MRA are more advanced computerized imaging studies that can provide detailed information on the blood vessels. These tests allow the vascular surgeon to see the vessels in 3 dimensions helping the surgeon decide on the best treatment options.
Angioplasty and stenting
Angioplasty uses an inflatable balloon catheter to open a narrowed vessel. Depending on the size of the plaque, the surgeon performing the procedure may decide to put a stent into the vessels to prevent it from closing up. With time, the blood flow in the affected area will be
restored. This is a surgical procedure that is performed in special laboratories or hospitals and requires anesthesia. You may have also had a stent placed. Please watch this video for more information:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UOXQbF3K56g
Atherectomy
This includes a number of treatment methods that use special wire/catheter to remove plaques from the affected arteries. The plaques can be scraped, shaved, or cut by special catheter devices. The vascular surgeon will decide which method is more suitable depending on the location and morphology of the plaques. These are surgical procedures that grew in popularity
because of the available novel devices.
Venous Disease
Our clinic has extensive experience in treating varicose vein disease, from the most complicated cases to the cosmetic conditions. In our clinic, we use multiple treatment modalities described in the text below to achieve the best results. Our physicians are affiliated with multiple hospitals and accept most insurance plans.
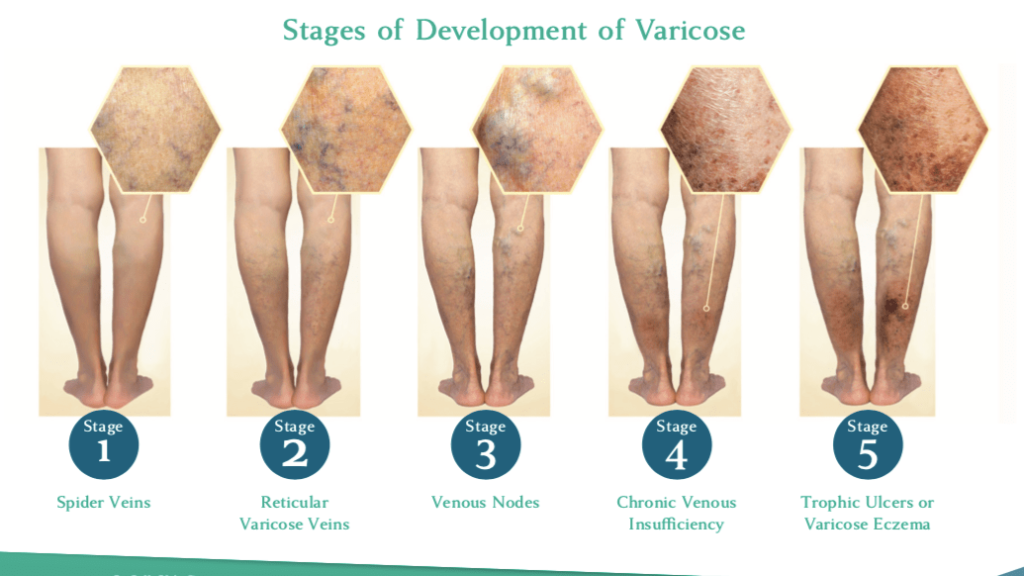
Venous disease affects millions of people around the world. It is a condition during which veins become enlarged due to various reasons and result in a number of symptoms. The most common symptoms are: leg pain, swelling, heaviness, especially at the end of the day, itching, night cramps, discoloration, and painful bulging veins. In later stages, patients may experience phlebitis (inflamed veins with redness and pain), lipodermatosclerosis (hardening and discoloration of the skin), and venous ulcers.
- There are a number of factors that can cause veins: genetics, fluctuating weight, prolonged periods of standing, prolonged periods of sitting with little to no movement, pregnancy
- Regardless of whether or not you have symptoms, ultrasound is still recommended as visible veins can be caused by insufficiency in the deeper veins that are not visible.
In most cases varicose veins are not serious, but they do worsen over time if left untreated. This can then cause symptoms such as:
Itching
Pigmentation around the ankles
Ulcers at the ankles or open sores
Pain
Swelling
Cramping
Aching
Itching
Heaviness or tiredness
Restlessness
The reasons for developing venous disease can be different. The most common ones are: hereditary – when your parents or close relatives have this issue; socio-economic – obesity, sedentary lifestyle or luck of exercise, jobs requiring prolonged standing (barbers, cashiers, baristas, nurses, surgeons, etc.).
In addition, venous disease can appear as part of other medical conditions, which lead to the elevation of venous pressure (heart conditions, etc.) or as part of cancer. Also, women are more prone to developing varicose veins than men because of female hormones and pregnancies.
Modern technologies have revolutionized the way venous disease is treated. To compare, a little over a decade ago, the treatment of venous disease was performed in hospitals and resulted in a long recovery period and could lead to many side effects.
Currently, due to the growth of improved technologies, such treatment has become a
simple, minimally invasive in-office procedure with a quick recovery period and minimal side effects. Typically, this procedure will take around 30 minutes. We have even seen cases when patients have returned to their normal activities the same day.
We get asked this question very often. There is no simple answer to this question.
Typically, the treated veins don’t come back. However, usually progressive varicose vein disease is seen in patients with genetic predisposition. Such patients may develop multiple new varicose veins. That is why we recommend having routine follow-ups with the treating physician so the new varicose veins can be diagnosed earlier and treated.
Please note that predisposed patients that have healthy food habits and exercise have a lower chance of recurrent disease.
There are multiple ways to treat varicose veins. Among those are laser treatment,
radiofrequency ablation, mechano-chemical occlusion, treatment with Varithena (similar to sclerotherapy), sclerotherapy, and microphlebectomy.
There is no such thing as better modality. They are usually used for different conditions. The only thing that matters is the experience of the physician and the crew. All the modalities can be successfully used in the hands of an experienced physician.
We recommend that the patients get treatment in a clinic that has experience with all the different treatment modalities because a combination of multiple modalities may be needed for best results.
Radio Frequency and Laser Ablation are minimally invasive varicose vein treatment procedures that use heat to collapse and seal off the targeted blood vessels. The ablated vein becomes a scar tissue and is absorbed by the body.
- Advantages: Effective and safe procedures with low complication rate and short recovery time.
- Disadvantages: Tumescent anesthesia is used, which requires several injections to deliver a fluid around the vein.
Mechano-Chemical Ablation with ClariVein®™ is one of the newest endovenous ablation technologies. ClariVein®™ combines two approaches, involving the use of a mechanical device to
destruct the vein to be treated, as well a sclerosing agent. ClariVein®™ is performed using a local anesthetic with ultrasound visualization of the veins.
- Advantages: No tumescent anesthesia is needed; the procedure usually takes less time.
- Disadvantages: Requires the use of a sclerosant (medication) to seal the vein. As with all medications, allergic reaction can occur.
Sclerotherapy involves an injection of a solution (we use Polidocanol) directly into the vein. The solution irritates the lining of the blood vessel, causing it to collapse and stick together forming a clot. With time, the clot is absorbed by the body.
- Advantages: Very popular and effective method to treat spider veins and larger veins that cannot be treated with other modalities.
- Disadvantages: Potential allergic reaction; staining (skin darkening) in some cases (especially in patients with lighter skin color).
Varithena® is a relatively new, nonsurgical minimally invasive method. Similar to
sclerotherapy, it involves an injection of a specially prepared solution (1%
Polidocanol) into a treated vein, which leads to collapsing of the vein and
forming a clot. With time, the occluded vein is absorbed by the body.
- Advantages: Nonsurgical, minimally invasive, and quick procedure.
- Disadvantages: Potential allergic reaction and discoloration.
What to Expect on Your Visit
You will meet one of our physicians in the office for a consultation. If a venous disease is suspected, an ultrasound test will be performed and will take about 20 minutes. This test is not painful and is safe. For best results, this test is performed in a standing position. It can be repeated multiple times if needed.
Based on the information of the test, the doctor will present you with a treatment plan, which will be submitted to the insurance company for approval. Once it is approved, you will be contacted to start the treatment.
Typically, the treatment of varicose veins may take from 1 to 6 weeks. In complex cases, it may take longer.
- Depending on the doctor’s availability, you may be seen after the ultrasound is completed. If the doctor is unavailable to read the us right away, you will be asked to come back for results within 1 week.
- You will be given shorts to put on for the ultrasound. Wear comfortable and loose-fitting clothing. If undergarments are too long or tight, you will be asked to remove them during the ultrasound. It is recommended to have food prior to the ultrasound.
The ultrasound is normally performed in standing position. Be prepared to stand on pedestal. There will be a bar handle to hold onto.
- No. Ultrasound is non-invasive and is performed with water-based hypoallergenic gel. The ultrasound probe is placed on the legs and light pressure is applied. Please notify your ultrasound technician if there
are any special conditions he/she needs to know of prior to beginning the scan.
- Approximately 25-40 minutes.
Depending on your insurance, you may be asked to wear compression socks for a period of time, then be asked to come back for a follow up visit with the provider. If then, the doctor finds that treatment is best, he/she will recommend moving forward with one of the procedures best fit for you.
Most medical insurances, including medicare will normally cover the cost of ultrasound visits and procedures. Prior authorization will be obtained by the office; pre-authorizations do not guarantee payments, as this is determined by factors provided by the office to the insurance company. The insurance company will determine payment if procedure is deemed to be medically necessary. Cost of compression stockings is normally not covered by insurance.
However, the different insurance plans may have different guidelines for covering the treatment. It mostly depends on the way the treatment plan is presented to the payor.
Our team has a broad experience in working with various insurance plans and has a low denial rate. Our team members will guide you through the process and obtain the best possible coverage from your insurance provider.
No. In fact, we recommend that you have a light meal or snack prior to your procedure.
No. There is no down time after either of the venous procedures. They are minimally invasive and performed under local anesthesia. You will be asked to walk for 10-15 minutes before leaving the office
right after your procedure.
Expect to be in office for 1-2 hours.
Depending on the length of the vein and the specific procedure performed, expect the procedure itself to be approximately 20-40 minutes.
Your leg after most procedures will be wrapped or in compression stocking. You will need to keep the leg wrapped overnight for the first 24 hours, then 7 days only during the day. After the initial 24 hours, you may take a shower. Refrain from hot tubs and saunas for at least 2 weeks after your procedure. It is important to walk regularly right away. Refrain from heavy lifting and heavy exercises that exceed lifting 20 pounds during the first 2 weeks.
You will be asked to come back for your post-operative ultrasound 3-7 days after the procedure. The ultrasound will be 10-15 minutes. This ultrasound will only be performed within the area of the procedure. If there are no complications, you can continue treatment right away on your next visit.
You may contact the office anytime on weekdays from 9:00am-5:00pm. If you have an emergency, you should call 911 go to the nearest urgent care center.
